How to operate a drone unveils the exciting world of unmanned aerial vehicles. This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and controls to advanced techniques and safety regulations. We’ll explore the intricacies of various drone components, flight modes, and photography/videography capabilities, ensuring you’re well-equipped to take to the skies responsibly and confidently.
Whether you’re a novice eager to learn or an experienced pilot looking to refine your skills, this guide offers valuable insights and practical advice. We cover everything from basic maneuvering and emergency procedures to advanced flight planning and aerial photography techniques. By the end, you’ll be ready to harness the power of drone technology for personal or professional use.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight capabilities and overall performance. This section will detail the function of key components, discuss propeller types, and compare the specifications of different drone models.
Drone Component Functions
A typical drone comprises several key components. The propellers generate thrust, powered by motors controlled by the flight controller. The battery provides the power source, while the GPS module (in GPS-enabled drones) aids navigation and stabilization. The camera, for photography and videography, is often integrated, and a transmitter allows remote control.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety protocols and legal requirements, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone before your first flight. This will ensure you operate your drone responsibly and safely.
Drone Propeller Types
Drone propellers come in various designs, each affecting flight characteristics. Standard propellers offer a balance of performance and efficiency. Low-pitch propellers generate more thrust at lower speeds, ideal for heavier payloads or calmer conditions. High-pitch propellers provide higher speed and efficiency but may sacrifice some lifting power. The size and material of the propeller also influence its performance and durability.
Comparison of Drone Models
The following table compares three popular drone models, highlighting their key features and specifications. These specifications can vary based on specific versions and configurations.
| Feature | Drone Model A | Drone Model B | Drone Model C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Flight Time | 30 minutes | 25 minutes | 40 minutes |
| Camera Resolution | 4K | 1080p | 4K |
| Maximum Speed | 60 km/h | 50 km/h | 70 km/h |
| Weight | 1.2 kg | 0.9 kg | 1.5 kg |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is paramount for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s physical condition, verifying battery health, and confirming environmental conditions are suitable for flight.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously follow this checklist:
- Inspect propellers for damage or cracks.
- Check motor mounts for tightness and security.
- Verify battery charge level and health.
- Examine the camera and gimbal for proper function.
- Confirm GPS signal is strong and stable (if applicable).
- Check the weather conditions – avoid strong winds or precipitation.
- Review local airspace restrictions and regulations.
Battery Health and Charging
Maintaining optimal battery health is crucial for extended flight times and safety. Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and avoid overcharging or discharging the battery. Store batteries in a cool, dry place to prevent degradation.
Taking Off and Landing
Proper takeoff and landing techniques are fundamental to safe drone operation. These procedures minimize the risk of damage to the drone and ensure a smooth flight experience. Understanding environmental factors is also key.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
For a safe takeoff, gently increase throttle until the drone lifts off vertically. Maintain a steady ascent and avoid abrupt movements. For landing, gradually decrease throttle until the drone touches down softly. Avoid sudden descents or hard landings.
Emergency Landing Procedures
In case of emergency, prioritize a safe landing. If control is lost, attempt to land the drone in a clear, open area. If the battery is critically low, execute an immediate, controlled descent.
Drone Controls and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding drone controls is essential for maneuvering the aircraft effectively and safely. This section explains the functions of control sticks and various flight modes.
Drone Control Stick Functions
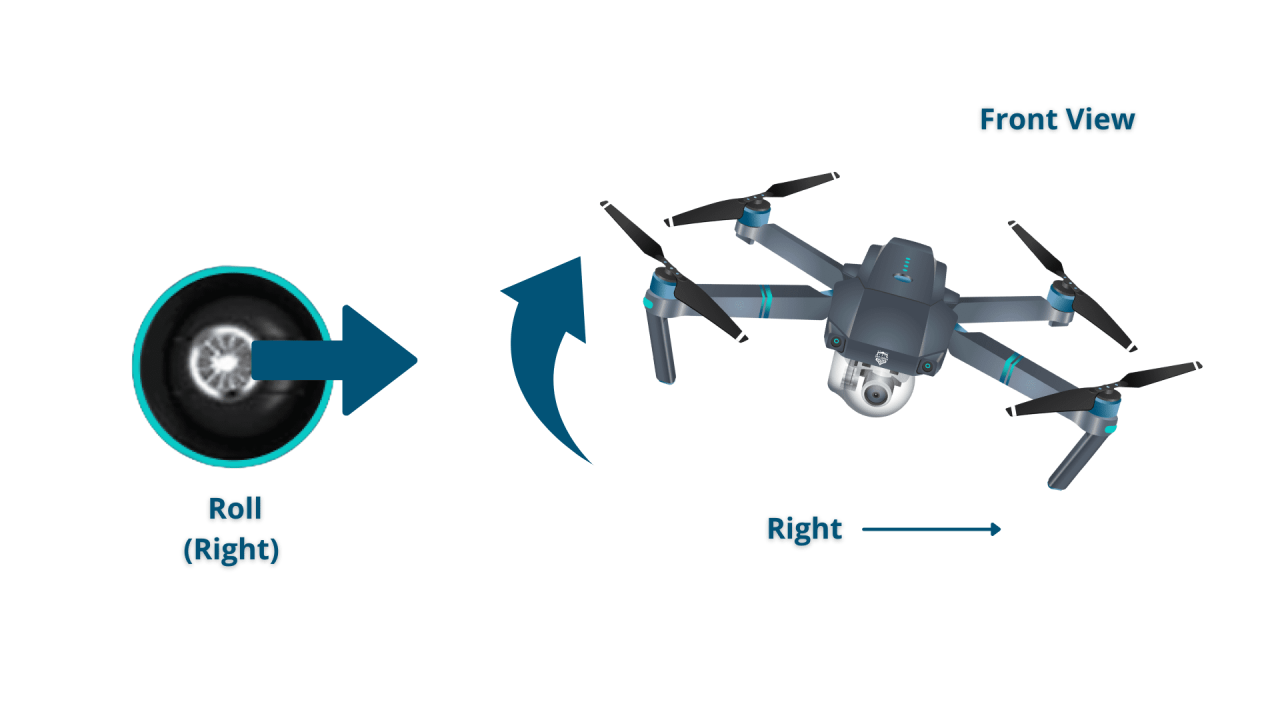
Most drone remotes use two joysticks. The left stick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right stick controls direction (forward, backward, left, right).
Drone Maneuvering
Moving the right stick forward moves the drone forward; backward moves it backward. Moving the right stick left or right moves the drone sideways. The left stick controls ascent and descent; twisting the left stick controls yaw.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. GPS mode utilizes GPS signals for precise positioning and stability. Attitude mode maintains the drone’s orientation relative to its starting position. Manual mode provides the most direct control but requires greater skill.
Flying in Different Environments
Operating a drone in various environments presents unique challenges. Understanding these challenges and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies is crucial for safe and responsible drone operation.
Flying in Windy Conditions, How to operate a drone
Strong winds can significantly impact drone stability and control. Avoid flying in high winds. If flying in light winds, adjust your flying style to compensate for wind drift.
Flying Near Obstacles

Flying near obstacles requires careful planning and precise control. Maintain a safe distance from obstacles and always be aware of your surroundings. Use visual observation and potentially obstacle avoidance features if available.
Flying in Populated Areas
In populated areas, adhere strictly to local regulations and maintain a safe distance from people and property. Be mindful of privacy concerns and avoid flying over private property without permission.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section will guide you through optimizing your drone’s camera for high-quality results.
Camera Settings Adjustment
Adjusting aperture, shutter speed, and ISO impacts image quality. A lower aperture (larger f-number) increases depth of field, while a higher shutter speed freezes motion. ISO controls sensitivity to light, with higher ISO values resulting in more noise.
Camera Angles and Shots
Experiment with various angles, such as high-angle shots for wide landscapes and low-angle shots for dramatic perspectives. Consider using different shots like panoramas and cinematic sequences.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as calibrating the drone and practicing maneuvers in a safe open area, is crucial before venturing out. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone.
Mastering these skills ensures safe and effective drone operation.
Tips for High-Quality Aerial Media
- Shoot in the best lighting conditions (golden hour).
- Use a neutral density filter to reduce light and allow for slower shutter speeds.
- Plan your shots carefully and compose thoughtfully.
- Practice smooth, controlled movements.
- Edit your footage to enhance its visual appeal.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition and extending its lifespan. This section details a maintenance schedule and common troubleshooting steps.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Inspect propellers, motors, and other components after each flight. Clean the drone regularly using a soft brush and compressed air. Calibrate the drone periodically as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Common issues include low battery life, motor malfunctions, and GPS signal loss. Consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide for specific solutions. If problems persist, seek professional assistance.
Cleaning and Storage
Clean the drone with a soft brush and compressed air. Remove any debris or dirt. Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Responsible drone operation involves strict adherence to local regulations and prioritizing safety. This section highlights the importance of responsible drone use and potential consequences of non-compliance.
Local Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions

Before flying, thoroughly research and understand local regulations and airspace restrictions. These regulations vary by location and may prohibit flying in certain areas or at certain altitudes.
Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible drone operation prioritizes safety, respects privacy, and adheres to all applicable laws. It involves careful planning, pre-flight checks, and responsible flying practices.
Consequences of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can lead to fines, confiscation of the drone, and even criminal charges. Always prioritize safe and legal operation.
Advanced Drone Techniques
This section explores more complex flight planning and execution, including waypoint navigation and advanced maneuvers.
Complex Drone Flight Planning
Planning complex flights involves careful route mapping, considering obstacles, and ensuring sufficient battery life. Waypoints help automate the flight path.
Waypoint Navigation and Automated Flight Planning Software
Waypoint navigation uses pre-programmed points to guide the drone along a specific path. Automated flight planning software simplifies route creation and ensures smooth transitions between waypoints.
Aerial Maneuvers
Depending on the drone model, advanced maneuvers such as flips and rolls might be possible. These require practice and skill to execute safely and smoothly.
Drone Battery Management
Proper battery care is crucial for extending battery life and ensuring safe operation. This section details best practices for charging, storing, and maintaining drone batteries.
Importance of Proper Battery Care
Proper battery care maximizes flight times and battery lifespan. Avoid overcharging, deep discharging, and extreme temperatures.
Charging and Storing Drone Batteries Safely
Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow charging instructions carefully. Store batteries in a cool, dry place at a partially charged state (around 50%).
Comparison of Drone Battery Types
Different battery types offer varying capacities, weights, and discharge rates. LiPo batteries are commonly used in drones.
| Battery Type | Capacity (mAh) | Weight (g) | Discharge Rate (C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo Battery A | 1500 | 150 | 30C |
| LiPo Battery B | 2200 | 200 | 45C |
| LiPo Battery C | 3000 | 250 | 60C |
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with responsible practice. This guide has equipped you with the fundamental knowledge and practical techniques needed to safely and effectively operate a drone. Remember to always prioritize safety, adhere to local regulations, and continue learning to expand your capabilities. The skies await!
FAQ Overview
What is the maximum flight time for most drones?
Flight time varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge, but always check your specific drone’s specifications.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and registration procedures.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Immediately attempt to regain control using the emergency landing procedure Artikeld in your drone’s manual. If unsuccessful, try to locate the drone using its GPS tracking features (if available). Report the incident to the relevant authorities if necessary.
What are the common causes of drone crashes?
Common causes include low battery, pilot error (lack of skill or awareness), mechanical failure, and adverse weather conditions. Regular maintenance and proper pre-flight checks can minimize these risks.
